 We have 206 or more bones in our bodies. Our bones are made of collagen which is a protein and calcium phosphate which is a mineral. The calcium is what makes our bones strong and hard. We cannot make calcium so we must eat or drink foods to get the calcium we need. In addition to being an important substance in the bones, calcium is also used by our bodies to help our muscles and nerves work properly and to assist us in healing wounds. When our bodies need calcium it is taken from the bones and a low level of calcium in our bodies can lead to brittle soft bones that can break or fracture easily.
We have 206 or more bones in our bodies. Our bones are made of collagen which is a protein and calcium phosphate which is a mineral. The calcium is what makes our bones strong and hard. We cannot make calcium so we must eat or drink foods to get the calcium we need. In addition to being an important substance in the bones, calcium is also used by our bodies to help our muscles and nerves work properly and to assist us in healing wounds. When our bodies need calcium it is taken from the bones and a low level of calcium in our bodies can lead to brittle soft bones that can break or fracture easily.
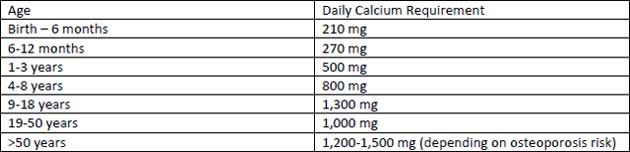
Osteoporosis is a disease that occurs when the bones are weak and deficient in the calcium needed to keep them strong. While there are several causes of osteoporosis, inadequate calcium intake can certainly lead to it and one of the first steps in treatment is to make sure your dietary calcium intake is adequate. It is important to remember that how much calcium we actually need depends on a number of factors including age, gender and pregnancy. The following is a guideline to how much calcium is needed by different age groups:
Our primary source of calcium should be in the foods we eat and drink. Excellent sources of calcium include dairy products like milk, yogurt and cheese. Other great sources are tofu, green leafy vegetables like spinach, kale and mustard greens, broccoli and almonds. Remember that calcium enriched foods like orange juice with calcium and calcium enriched almond mild are other excellent sources. When we cannot get all the calcium we need from food, supplements like calcium carbonate and calcium citrate can help to insure adequate calcium intake. Calcium carbonate should be taken with food. Calcium citrate can be taken with or without food It is also important to remember that we need Vitamin D to help us absorb calcium. The National Osteoporosis Foundation recommends 400- 800 IU of Vitamin D for people under the age of 50 and 800 to 1000 IU of Vitamin D for all adults over 50. Unfortunately, doctors are beginning to diagnose Vitamin D deficiency in more people and getting Vitamin D levels and treating deficiency is becoming a focus of attention. While we can make Vitamin D with 10-15 minutes of sun exposure daily, our ability to do this decreases over time. Excellent sources of Vitamin D in food include milk, tuna fish and eggs.
Click on the links below to learn more about Calcium and Vitamin D:
